August 1916 marked two years of war and was little different from the month before or the one to follow. On the Somme front the Battles of Delville Wood and Poziéres continued, piling up casualties for little gain and emulating the ongoing action to the south at Verdun. There on 1 August the Germans launched a surprise assault on Fort Souville and were duly counterattacked by the French, who on 18 August recaptured Fleury – or what was left of it.
On 29 August Verdun claimed a major German casualty when Falkenhayn was sacked as Chief of Staff and replaced by Hindenburg. The apparent failure of the Verdun campaign and the beginning of the Somme and Brusilov Offensives played into the hands of Hindenburg and Ludendorff, who had been conspiring against Falkenhayn. Ludendorff became First Quartermaster-General, but he was in fact the real power, rapidly assuming control of the entire military and ultimately the Reich itself.
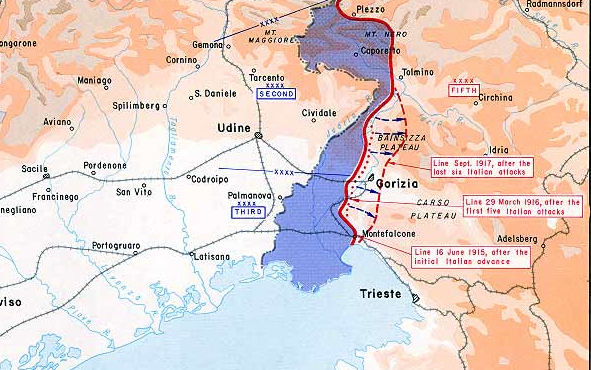
To the south the Isonzo Follies started up again as General Cadorna sought to take advantage of an Austrian line weakened by the removal of troops for the Trentino Offensive. The Sixth Battle of the Isonzo (or Battle of Gorizia) kicked off on 6 August with a two pronged assault against the long-sought prize of Gorizia, which the Austrians abandoned on 8 August. Gorizia was the gateway to Trieste and Ljubljana, but the poorly equipped Italian troops could make no further headway and Cadorna ended the offensive on 17 August.
This was Cadorna’s first success, and Italian morale skyrocketed with the capture of the city they had wanted since 1914. But they wanted Gorizia in order to seize Trieste and invade Slovenia, and in fact that would never happen, leaving Cadorna with only a wrecked city and more dead: 21,000 (not counting the missing) to the Austrian’s 8000. Throwing 22 divisions against 9 Austrian allowed the (limited) breakthrough to Gorizia, but Cadorna’s frontal assaults were extremely costly.
Not costly enough, however, to prevent Rome from sending troops to join the growing international camp at Salonika on 12 August, presumably to back up Italian claims in the western Balkans. On 28 August Italy declared war on Germany, apparently under pressure from the Allies, since the two countries were not in direct conflict (German troops would not appear on the Italian front until 1917) and actually benefited from non-belligerence.
Meanwhile, Greece tottered toward open participation in the war. National pride and the Bulgarians in Macedonia spurred the Venizelist (pro-Entente, anti-Royalist) forces clustered in Salonika, and on 29-30 August Venizelist officers, supported by the Allies, launched a successful coup against the loyalists. Troops across northern Greece joined the revolt, and the seed of a government in opposition to Athens, the “National Defense Committee,” was formed. Loyalist officers fled south.
To the south the Turks, who had been steadily creeping across Sinai during July, took what would be a final shot at the Suez Canal on 3 August, advancing towards Romani, about 20 miles from the Canal. The British had been busy, however, building a rail line east out of Kantara and could now send out more substantial forces. The result was the Battle of Romani on 3-5 August, during which the Turkish army was decisively defeated, suffering 9200 casualties to the Allied 1130. But the Ottoman commander, Friedrich Kress von Kressenstein, had prepared fortified positions during his advance, and his surviving forces were able to execute an orderly retreat. Nevertheless, by 12 August the Turks had been driven all the way back across Sinai to El Arish. The Battle of Sinai had ended and the Battle for Palestine could begin.
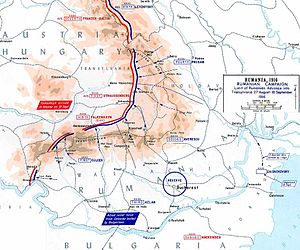
The big news of August 1916 was the entrance of Romania into the war. King Carol I, a Hohenzollern like the Kaiser, had signed a defensive alliance with the Central Powers, but in 1914 the Romanian people favored the Allies and Romania remained neutral. King Ferdinand I, who succeeded Carol in October 1914, was more inclined towards the Entente and wanted Transylvania, an Austrian province with a Romanian population, but was wary of the Russians and being left in the lurch by the French and British. Only after the Allies agreed to stringent terms (most of which were subsequently ignored) did he make his move.
An alliance was made with the Entente on 17 August, and on the 27th Romania declared war on Austria-Hungary and began mobilization. The next day a Romanian army invaded Transylvania, prompting Germany to declare war; Turkey followed on 30 (?) August and Bulgaria on 1 September. September would not be a good month for the Romanians.
Oh, the South Africans and Belgians continued capturing towns in East Africa, but Lettow-Vorbeck continued to lead them on a merry chase.